Overview
Deformers are the commands that attach the rig to the scene geometry.
They are executed after the construction of the template hierarchy and the modifiers.
Creation and Editing
Deformer commands work in a similar way to modifiers, but they are a bit more complex to create.
They are only executed once they are placed on a node in the template hierarchy.
To create a deformer, you must use the Mikan save functions, available in the Deformers tab.
- Select a geometry (or a group containing multiple geometries).
- Click the Create Backup Group button.
- Place the backup group and its notes inside the template hierarchy.
The root of the deformer group (whose name starts with _) contains additional information:
it stores the path of the selected node to help resolve name duplicates when restoring geometries.
If multiple deformers are saved for the same geometry, they will be listed sequentially in the notes.
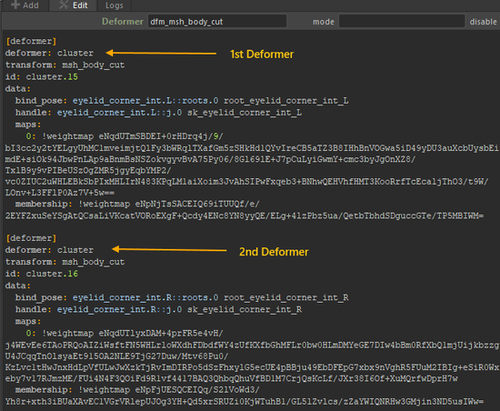
This allows them to be rebuilt in the correct order during the build process.
However, if the deformers are not connected linearly, you will need to manually update the notes to define the correct inputs/outputs (Mikan does not yet save this information).
IDs, Options and Hooks
Since deformer node structures differ greatly between software, Mikan cannot rely on native attributes directly.
To ensure deformers are portable and reproducible across DCCs, each deformer is defined using three concepts: IDs, Options, and Hooks.
-
IDs: each deformer receives a unique identifier when it is saved (or recreated).
The ID consists of:- the geometry name (or full path)
- its tag (see the Mikan Identifiers page here IDs)
tipIf you select a mesh and open its modifier note, you can see the IDs of all the deformers applied to that mesh in the Template tab.
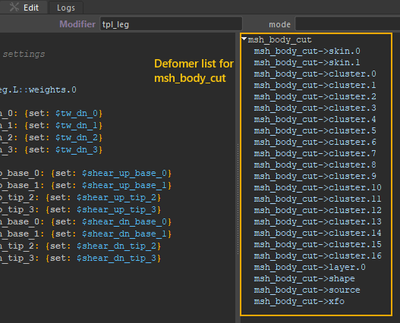
Because the list of available attributes also differs between software, Mikan uses a specific nomenclature for them.
-
Options: standardized creation parameters of the deformer (e.g. subdivision level, curvature, list of influence joints).
These are saved in the template notes and rebuilt consistently across applications. -
Hooks: attributes exposed for rig connections (e.g. envelope, weight, curvature).
Hooks define the animator-facing interface and remain uniform regardless of the underlying software.
This approach ensures that deformers in Mikan remain software-agnostic while providing a stable and predictable workflow.
The detailed list of options and hooks is documented in the dedicated pages for each deformer.
Linked Backup
When creating a “linked” deformer group (chain icon), the group itself receives a unique identifier, which it then propagates to all deformers saved or built within it.
- This mode saves only the new deformers present in the scene.
- It first scans the existing deformers already saved in the template hierarchy to prevent duplicates.
The purpose of this mode is to prevent saving deformers that are already linked to a group and to avoid duplicate notes.
This mode is especially useful for handling character variations.
For example:
- Original character
- Variant with an added hat
If you select the top node of the modeling hierarchy, Mikan will only save the deformers applied to the hat.
This way, you can clearly distinguish the original character's deformers from those of the additional elements in the variation.
During the rebuild process, Mikan will automatically link the deformers.
Therefore, it is generally recommended to use classic backups for your main scenes to ensure that all deformers are saved.
The linked backup mode should be reserved for specific variation cases only.